 Frederic Noy
Book
Frederic Noy
Book
02/01/2009
Rony Brauman
Humanitarian medicine is intented for marginalized people, hit by a crisis or deprived of access to medical care. This book helps us understand how the specificity of humanitarian medicine stems from real-life situations, more than from the medical act in itself.
 Wairimu Gitau/MSF
Interview
Wairimu Gitau/MSF
Interview
11/30/2022
Pierre Mendiharat
Elba Rahmouni
Léon Salumu Luzinga
This article was published on December 22nd, 2021, in the Journal of Humanitarian Affairs (Issue 3, Volume 3).
Despite a concerted international effort in recent decades that has yielded significant progress in the fight against HIV/AIDS, the disease continues to kill large numbers of people, especially in certain regions like rural Ndhiwa district in Homa Bay County, Kenya. Although there is still no definitive cure or vaccine, UNAIDS has set an ambitious goal of ending the epidemic by 2030, specifically via its 90-90-90 (treatment cascade) strategy – namely that 90 per cent of those with HIV will know their status; 90 per cent of those who know their status will be on antiretroviral therapy and 90 per cent of those on antiretroviral therapy will have an undetectable viral load. These bold assumptions were put to the test in a five-year pilot project launched in June 2014 by Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF) and Kenya’s Ministry of Health in Ndhiwa district, where an initial NHIPS 1 study by Epicentre (MSF’s epidemiology centre) in 2012 revealed some of the world’s highest HIV incidence and prevalence, and a poor “treatment cascade”. Six years later a new Epicentre study, NHIPS 2, showed that the 90-90-90 target had been more than met. What explains this ‘success’? And given the still-high incidence, is it truly a success? What follows is an interview on the political, scientific, and operational challenges of the Ndhiwa project with MSF Deputy Director of Operations Pierre Mendiharat and physician Léon Salumu, Head of MSF France Kenya programs, conducted by Elba Rahmouni.
 MSF
Analysis
MSF
Analysis
11/04/2022
Natalie Roberts
This article was published on December 22nd, 2021 in the Journal of Humanitarian Affairs (Issue 3, Volume 3).
In this article, Natalie Roberts analyses the actions and positioning of MSF during the Ebola outbreak in Nord Kivu (Democratic Republic of Congo, 2018-2020).
 Jean-Christophe Nougaret/MSF
Analysis
Jean-Christophe Nougaret/MSF
Analysis
11/14/2021
Elba Rahmouni
Pierre Mendiharat
Léon Salumu Luzinga
This article was first released in the 18th volume of the Humanitarian Alternatives magazine. Designed to reduce the incidence of HIV/AIDS in a Kenyan district, a Médecins Sans Frontières project successfully exceeded the “90-90-90” target set by UNAIDS. A look back on the results that the authors of this article - Pierre Mendiharat, Deputy director of operations at MSF France and Léon Salumu Luzinga, Program manager at MSF France, interviewed by Elba Rahmouni - believe are encouraging but by no means a guarantee that the epidemic will be over by 2030.
 Mohamad Cheblak/MSF
Review
Mohamad Cheblak/MSF
Review
05/07/2021
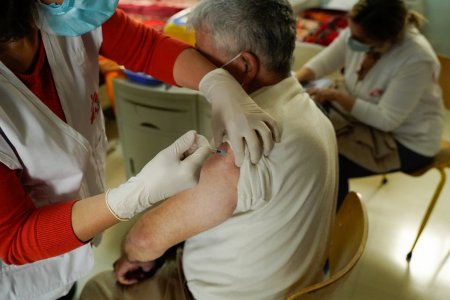
Michaël Neuman
Natalie Roberts
We can all agree that the emergence of Covid-19 vaccine is “an absolutely astonishing development”, but vaccines are unlikely to completely halt the spread of the virus, let alone eradicate it. Yet even without achieving herd immunity, the ability to vaccinate vulnerable people seems to be reducing hospitalizations and deaths from Covid-19.
 Clément Mahoudeau/MSF
Analysis
Clément Mahoudeau/MSF
Analysis
12/02/2020
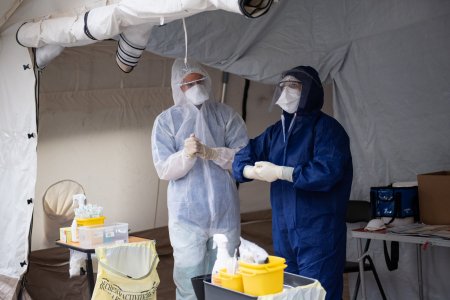
Michaël Neuman
Emmanuel Baron
In this paper, the two authors examine certain aspects of the French response to the epidemic in the light of the experience of Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF) in that field, primarily with respect to the relationship between the actors of the response and the beneficiaries.
 Mariana Abdalla/MSF
Opinion
Mariana Abdalla/MSF
Opinion
02/19/2021
Jean-Hervé Bradol
Isabelle Defourny
Blog written by Jean-Hervé Bradol, director of studies at the Crash.
Today, in order to obtain supplies of vaccines against Covid-19, there is neither a major difficulty related to price, nor a major obstacle related to intellectual property rules, nor a deficit in bio-medical research. However, these three topics are generally at the heart of MSF's communication in the area of access to medical care for those in most need. Our discourse must therefore evolve.
With the emergence of worrying variants of the virus present in the early stages of the pandemic and, as a consequence, the need to vaccinate on a global scale as quickly as possible, the world is facing a double challenge: biological engineering and ultra-industrial production – “ultra” echoing the need to produce on a global scale in a short period of time.
 Giuseppe La Rosa/MSF
Interview
Giuseppe La Rosa/MSF
Interview
02/17/2012
Rony Brauman
In this interview conducted by Claudine Vidal in 2012 and published in the book Agir à Tout Prix (Humanitarian Negotiations Revealed: the MSF experience), Rony Brauman speaks about emergency humanitarian aid set up following natural disasters. Time constraints, access to victims, cooperation with local institutions, misleading representations of the disasters' effects, controversial assessments of the number of casualties; various topics related to these interventions are discussed and illustrated with specific examples.
 MSF/Rowan Pybus
Analysis
MSF/Rowan Pybus
Analysis
07/22/2020
Marc Le Pape
In France, from March onwards, many sociologists regularly appear in the media. Based on this observation, Marc Le Pape analysed 37 articles written during the containment period, dealing with the Covid-19 pandemic.
 Eric Bouvet
Interview
Eric Bouvet
Interview
05/11/2020
Emmanuel Baron
Elba Rahmouni
Crisis situation, response strategies, hydroxychloroquine, interventional epidemiology and the state of scientific research in Africa: Elba Rahmouni interviews Emmanuel Baron, Director of Epicentre, Médecins Sans Frontières
 Olmo Calvo/MSF
Opinion
Olmo Calvo/MSF
Opinion
05/10/2020
Jean-Hervé Bradol
The biggest oversight in the response to this epidemic has been the EHPADs. For the staff, the directive was clear: continue to work and provide an alternative to hospitalisation. No matter the conditions. For the residents, it was to die alone without treatment to alleviate their suffering.
 Eric Bouvet
Interview
Eric Bouvet
Interview
05/11/2020
Emmanuel Baron
Elba Rahmouni
Crisis situation, response strategies, hydroxychloroquine, interventional epidemiology and the state of scientific research in Africa: Elba Rahmouni interviews Emmanuel Baron, Director of Epicentre, Médecins Sans Frontières
 Frederic Noy
Book
Frederic Noy
Book











